艾克学院
什么是“甲基化”?
我们如何精确探索身体内的变化?
什么是DNA甲基化?
DNA甲基化是一种主要的表观遗传修饰,甲基化模式的改变在肿瘤发生发展中起着关键作用。由于DNA甲基化几乎存在于包括癌前病变的肿瘤发生发展全程,因此它可能是癌症早期诊断的理想生物标志物。在许多样本类型的肺癌中,各种异常的基因启动子甲基化被评估为生物标志物[1]。
一管血发现肿瘤踪迹
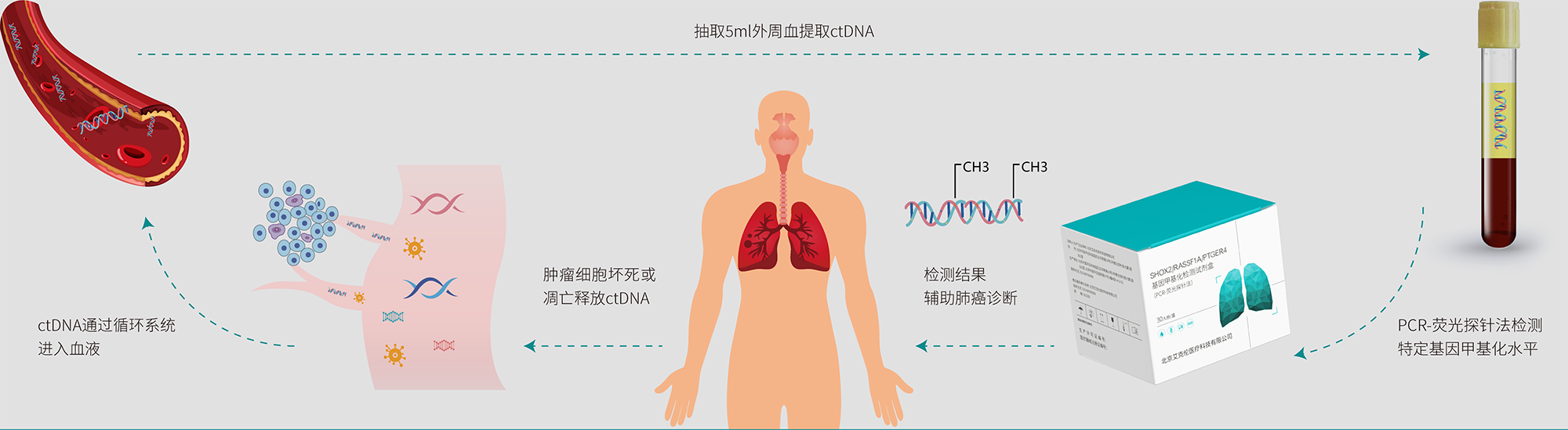
携带着遗传信息和表观遗传学改变的肿瘤细胞坏死或凋亡后,会向外周血中释放片段化的基因组DNA,即循环肿瘤 DNA (ctDNA)[2]。通过捕获这些微量 ctDNA,检测其特异性肿瘤甲基化位点改变,相较于传统检测技术,可更早、 更精准的检测肿瘤的发生和发展信息[3]。
参考文献:
[1] Rajabi H , Tagde A , Alam M , et al. DNA methylation by DNMT1 and DNMT3b methyltransferases is driven by the MUC1-C oncoprotein in human carcinoma cells[J]. Oncogene, 2016.
[2]Wan, J.C.M. et al. (2017) Liquid biopsies come of age: to-wards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat.Rev. Cancer 17, 223–238
[3]Gao Y, et al. Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing analysis of circulating tumour DNA for the detection and molecular classification of cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2022 Aug;12(8):e1014.